Working with Resources
Resources is a module for managing project assets. It allows you to:
- assign one or multiple resources to tasks, edit and delete assignments
- evaluate resources load per day via a special diagram
- display all resources and their related tasks in a dedicated view.
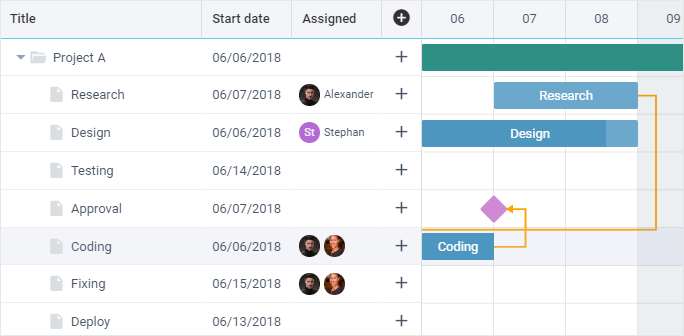
Enabling Resources
To enable resource management, set the resources property to true. Gantt will load resources from the corresponding URLs and allow users to assign or unassign them and allocate work load via the interface.
webix.ui({
view: "gantt",
url: "https://docs.webix.com/gantt-backend/",
// enable resources
resources: true,
});
Data Structure
If resources are enabled, Gantt will load resources, categories and assignments from the following URLs.
- resources - url/resources - resources themselves
- categories - url/categories - the groups the resources belong to
- assignments - url/assignments - relations between resources and their tasks.
Resources
When loading resources, Gantt expects JSON data where each element of the array is an object with the following fields:
- id (string, number) - resource ID
- name (string) - resource name
- avatar (string) - URL to the resource avatar
- category_id (string, number) - ID of the category the resource belongs to
- unit (string) - optional. Unit to measure resource in. If not set, unit will be taken from resource category or Gantt defaults.
JSON example
[
{
"name": "John",
"category_id": "1",
"avatar": "remote/image",
"id":"1"
},
// other resources
]
Categories
When loading categories, Gantt expects JSON data where each element of the array is an object with the following fields:
- id (string, number) - category ID
- name (string) - category name
- unit (string) - optional. Unit to measure resources of this category in. If not set, unit will be taken from Gantt defaults.
JSON example
[
{
name: "QA",
unit: "hour",
id: "1"
}
// other categories
]
Assignments
When loading assignments, Gantt expects JSON data where each element of the array is an object with the following fields:
- id (string, number) - assignment ID
- resource (string, number) - ID of the resource assignment belongs to
- task (string, number) - ID of the task assignment is linked to
- value (number) - value of the unit defined by the
unitfield in categories. It shows how much of this resource is required for a particular task.
JSON example
[
{
id: "3",
resource: "8",
task: "1.1",
value: 8
}
// other assignments
]
Calendars
Working calendars are loaded when the resourceCalendars property is enabled. Gantt expects JSON data where each element of the array is an object with the following fields:
- id (number) - calendar ID
- weeksDays (string) - working week days
- holidays (string) - optional. An array of holidays.
JSON example
[
{
id: 2,
weekDays: "1,2,3,4",
holidays: "2021-06-07,2021-06-12"
}
// other calendars
]
Note, that enabling calendars allows you to pass calendar ID to the desired resource object:
{
id: 3,
name: "John",
category_id: 1,
calendar_id: 1 }
In this case the resource with the ID of 3 will have working hours and holidays defined by the calendar with ID of 1.
Working with Local Data
When data is loaded to the client, you can access it via the Local service. Read more about services and their purposes in the dedicated article.
How to get Resources
All the resources are stored in a DataCollection.
The collection is accessible via the resources() method of the Local Data service.
const resources = $$("gantt").getService("local").resources();
To make sure that the data are already loaded, use the waitData() method to wait for a data promise.
const resources = $$("gantt").getService("local").resources();
resources.waitData.then(() => {
resources.getItem(resources.getFirstId()); // get first resource
});
You can get an array of all resources by serializing the collection:
Serializing resources collection
const resources = $$("gantt").getService("local").resources();
resources.waitData.then(() => {
const arr = resources.serialize();
/*[
{
category: "Design",
category_id: "3",
id: "7",
name: "Alina",
unit: "hour"
},
// ...
]*/
});
How to Get Resources of a Particular Task
To retrieve resources of a particular task, call the getAssignments() method passing the ID of the task as a parameter:
const taskAssignments = $$("gantt").getService("local").getAssignments(taskID);
The method returns a promise with an array of resources of the specified task. Each array element is an object with the following fields:
- avatar (string) - URL to the resource avatar
- category (string) - name of the category resource belongs to
- category_id (string, number) - ID of the category resource belongs to
- id (string, number) - assignment ID
- name (string) - resource name
- resource (string, number) - resource ID
- task (string, number) - task ID
- unit (number) - unit the resource is measured in
- value (number) - value of the unit.
const taskAssignments = $$("gantt").getService("local").getAssignments(1.1);
taskAssignments.then(taskData => {
const consumingTasks = taskData.filter(task => task.value > 5);
/*
[
{
avatar: "remote/avatar.jpg"
category: "QA"
category_id: "1"
id: "Ofmfy7ZsPuBN7dHR"
name: "John"
resource: "1"
task: "1.1"
unit: "hour"
value: 8
},
// other
]
*/
});
How to Get Categories
All the categories are stored in a DataCollection.
The collection is accessible via the categories() method of the Local Data service.
const categories = $$("gantt").getService("local").categories();
To make sure that the data are already loaded, use the waitData() method to wait for a data promise.
const categories = $$("gantt").getService("local").categories();
categories.waitData.then(() => {
categories.getItem(categories.getFirstId()); // get first category
});
You can get an array of all categories by serializing the collection:
Serializing categories collection
const categories = $$("gantt").getService("local").categories();
categories.waitData.then(() => {
const arr = categories.serialize();
/*[
{
id: "1",
name: "QA",
unit: "hour"
},
// ...
]*/
});
Related sample: Gantt: Operations with Resources
Resources View
By default Gantt displays tasks in the tree and chart. You can switch to the Resources view and instead of tasks show resources. In the tree they are arranged as projects with children as their related tasks. Correspondingly, resources chart will display tasks per assignees. There is also a separate group called Unassigned to track tasks that have not been assigned yet.
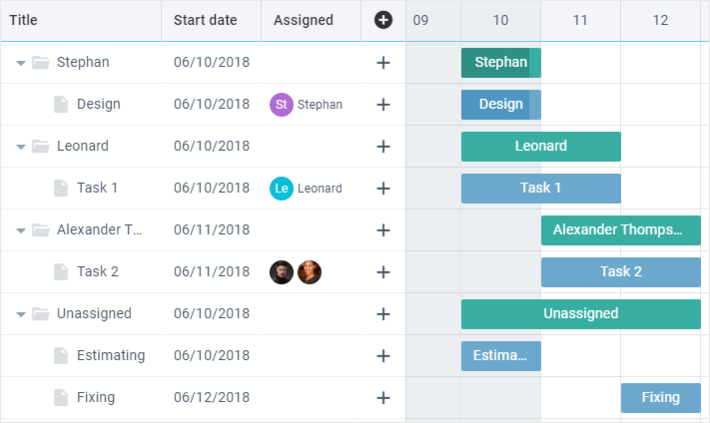
As far as resources are enabled (resources: true), you can switch to the Resource Tree by setting the display property to "resources":
webix.ui({
view: "gantt",
url: "https://docs.webix.com/gantt-backend/",
resources: true, // must be enabled!
display: "resources",
});
Resources Load Diagram
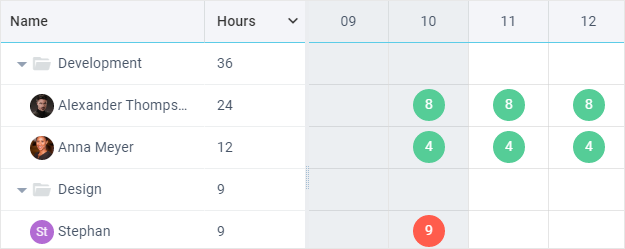
Resources Diagram is a separate view that allows you to:
- display working hours per category and resource
- display resources work load in hours or tasks
- visualize overload
The diagram is enabled via the resourcesDiagram property:
webix.ui({
view: "gantt",
url: "https://docs.webix.com/gantt-backend/",
resources: true, // must be enabled!
resourcesDiagram: true
});
Helpers for Resources
The Helpers service stores:
- default resource unit, which is "hour"
- default value of this unit, which is 8
- min and max values that user can set for the resource via the interface, which are [0, 24].
Via the service you can set a custom default resource value and the corresponding ranges (e.g. percent):
class MyHelpers extends gantt.services.Helpers {
constructor() {
super();
// set "percent" as default resource unit
this.defaultResourceUnit = "percent";
// add default value for "percent" work load
this.defaultResourceValues.percent = 100;
// add "percent" range
this.resourceValueRanges.percent = [1, 100];
}
}
Related sample: Gantt: Percent as Resources Unit
Setting Max Working Time
With the Helpers service you can set custom max working time (e.g. if an employee works part-time):
class MyHelpers extends gantt.services.Helpers {
// "customMaxTime" field comes from the backend
// set "customMaxTime" as a default value
getDefaultResourceValue(obj) {
return obj.customMaxTime || super.getDefaultResourceValue(obj);
}
// set "customMaxTime" as a max value
getResourceValueRange(obj) {
if (obj.customMaxTime) return [0.5, obj.customMaxTime];
return super.getResourceValueRange(obj);
}
}
Related sample: Gantt: Max Working Time
Redefining follows the common customization rules.
Back to top